18 KiB
Pick-and-Place Tutorial: Part 2
This part assumes you have access to a functional ROS workspace. If you do not yet have a working ROS setup, refer to the Resources section below to get started.
If you're new to ROS, check out the Start Guide on the ROS Wiki to get started.
Steps covered in this tutorial include creating a TCP connection between Unity and ROS, generating C# scripts from a ROS message, and publishing and subscribing to a ROS Topic. These steps are adapted from the ROS–Unity Integration Tutorials.
Table of Contents
Part 2: ROS–Unity Integration
Quick Description:
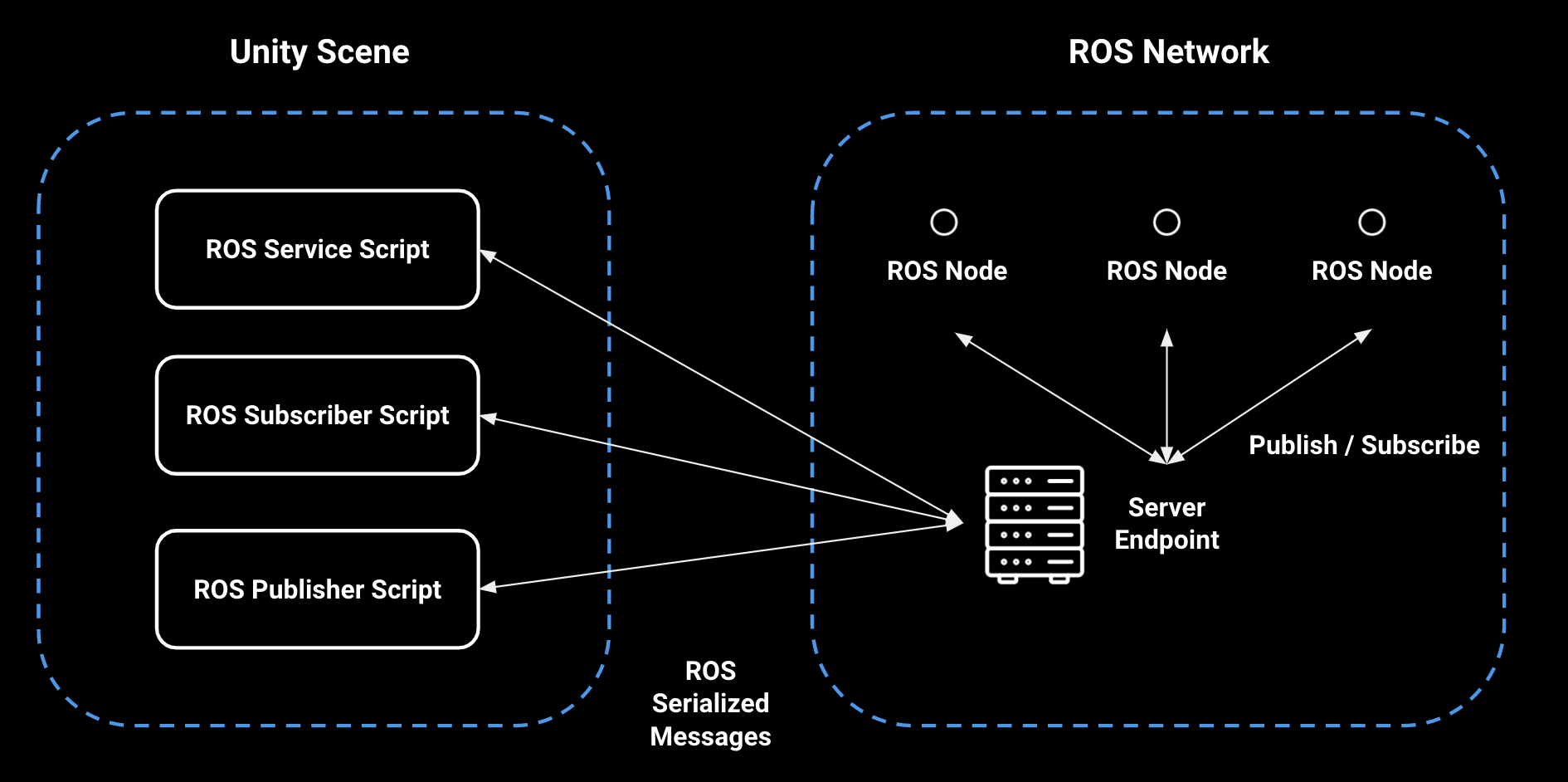
To enable communication between Unity and ROS, a TCP endpoint running as a ROS node handles all message passing. On the Unity side, a ROSConnection component provides the necessary functions to publish, subscribe, or call a service using the TCP endpoint ROS node. The ROS messages being passed between Unity and ROS are expected to be serialized exactly as ROS serializes them internally. This is achieved with the MessageGeneration plugin which generates C# classes, including serialization and deserialization functions, from ROS messages.
Setup
-
If you have not already, complete Part 1 to set up the Unity project.
-
Navigate to the
Unity-Robotics-Hub/tutorials/pick_and_place/ROSdirectory of this downloaded repo.- This directory will be used as the ROS catkin workspace.
- If you cloned the project and forgot to use
--recurse-submodules, or if any submodule in this directory doesn't have content, you can run the commandgit submodule update --init --recursiveto download packages for Git submodules. - Copy or download this directory to your ROS operating system if you are doing ROS operations in another machine, VM, or container.
- This contains ROS packages for the pick-and-place task, including ROS TCP Endpoint, Niryo One ROS stack, MoveIt Msgs,
niryo_moveit, andniryo_one_urdf.
The Unity Side
-
If the PickAndPlaceProject Unity project is not already open, select and open it from the Unity Hub.
Note: The Package Manager automatically checked out and built the ROS-TCP-Connection package in this project. You can verify this now by looking for
Packages/ROS-TCP-Connectorin the Project Browser or by opening the Package Manager window.The ROS-TCP-Connector package includes two pieces: TcpConnector, which contains the
ROSConnectionscript described above, and MessageGeneration, which generates C# scripts from ROS msg and srv files.Using this MessageGeneration component, three C# message scripts will be generated. Like their ROS msg counterparts, these scripts define the data values and contents that will be passed between Unity and ROS.
Note: Read more about the ROS msg here.
Note: Read more about the ROS srv here.
-
We will start with generating the MoveItMsg: RobotTrajectory.
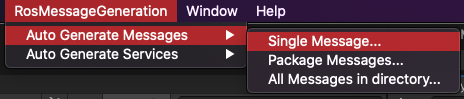
Select
RosMessageGeneration -> Auto Generate Messages -> Single Messagefrom the menu.In the Message Auto Generation window click
Browse File...and navigate to the MoveIt Msgs repository. Selectmoveit_msgs/msg/RobotTrajectory.msg, and then clickGENERATE!- One new C# script should populate the
Assets/RosMessages/Moveit/msgdirectory: RobotTrajectory.
Note: If any of these ROS directories appear to be empty, you can run the command
git submodule update --init --recursiveto download the packages via Git submodules. - One new C# script should populate the
-
Next, the custom message scripts for this tutorial will be generated.
Select
RosMessageGeneration -> Auto Generate Messages -> All Messages in Directory.In the Message Auto Generation window, click
Select Folder…and navigate to theniryo_moveitdirectory, e.g.Unity-Robotics-Hub/tutorials/pick_and_place/ROS/src/niryo_moveit/. Select themsgfolder, and then clickGENERATE!- Two new C# scripts should populate the
Assets/RosMessages/NiryoMoveit/msgdirectory: NiryoMoveitJoints and NiryoTrajectory.
MessageGeneration generates a C# class from a ROS msg file with protections for use of C# reserved keywords and conversion to C# datatypes. Learn more about ROS Messages.
- Two new C# scripts should populate the
-
Now that the messages have been generated, the service for moving the robot will be created.
In the menu, select
RosMessageGeneration -> Auto Generate Services -> Single Service. -
In the Service Auto Generation window, click
Browse File...and navigate to the niryo_moveit/srv directory, e.g.Unity-Robotics-Hub/tutorials/pick_and_place/ROS/src/niryo_moveit/srv. Choose theMoverService.srvfile, and then clickGENERATE!- Two new C# scripts should populate the
Assets/RosMessages/NiryoMoveit/srvdirectory: MoverServiceRequest and MoverServiceResponse.
MessageGeneration generates two C# classes, a request and response, from a ROS srv file with protections for use of C# reserved keywords and conversion to C# datatypes. Learn more about ROS Services.
- Two new C# scripts should populate the
-
In this repo, navigate to
Unity-Robotics-Hub/tutorials/pick_and_place. Select and copy theScriptsfolder and contents into theAssetsfolder of your Unity project. You should now find two C# scripts in your project'sAssets/Scripts.Note: The SourceDestinationPublisher script is included. This script will communicate with ROS, grabbing the positions of the target and destination objects and sending it to the ROS Topic
"SourceDestination_input". OnStart(), the TCP connector is instantiated with a ROS host name and port, and the articulation body values are assigned based on the GameObjects that will be assigned shortly. ThePublish()function is defined as follows:public void Publish() { NiryoMoveitJoints sourceDestinationMessage = new NiryoMoveitJoints(); sourceDestinationMessage.joint_00 = jointArticulationBodies[0].xDrive.target; sourceDestinationMessage.joint_01 = jointArticulationBodies[1].xDrive.target; sourceDestinationMessage.joint_02 = jointArticulationBodies[2].xDrive.target; sourceDestinationMessage.joint_03 = jointArticulationBodies[3].xDrive.target; sourceDestinationMessage.joint_04 = jointArticulationBodies[4].xDrive.target; sourceDestinationMessage.joint_05 = jointArticulationBodies[5].xDrive.target; // Pick Pose sourceDestinationMessage.pick_pose = new RosMessageTypes.Geometry.Pose { position = new Point( target.transform.position.z, -target.transform.position.x, target.transform.position.y ), orientation = pickOrientation }; // Place Pose sourceDestinationMessage.place_pose = new RosMessageTypes.Geometry.Pose { position = new Point( targetPlacement.transform.position.z, -targetPlacement.transform.position.x, targetPlacement.transform.position.y ), orientation = pickOrientation }; // Finally send the message to server_endpoint.py running in ROS ros.Send(topicName, sourceDestinationMessage); }This function first takes in the current joint target values. Then, it grabs the poses of the
targetand thetargetPlacementobjects, adds them to the newly created messagesourceDestinationMessage, and callsSend()to send this information to the ROS topictopicName(defined as"SourceDestination_input").Note: Going from Unity world space to ROS world space requires a conversion. Unity's
(x,y,z)is equivalent to the ROS(z,-x,y)coordinate. -
Return to the Unity Editor. Now that the message contents have been defined and the publisher script added, it needs to be added to the Unity world to run its functionality.
Right click in the Hierarchy window and select "Create Empty" to add a new empty GameObject. Name it
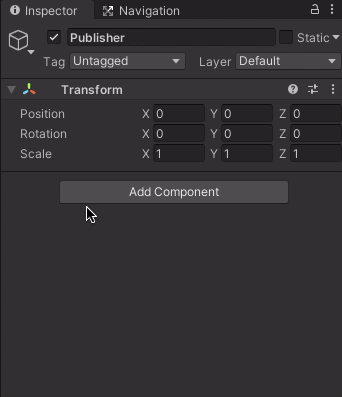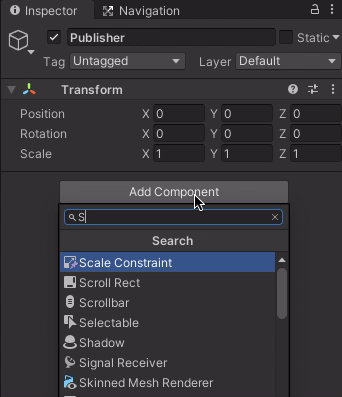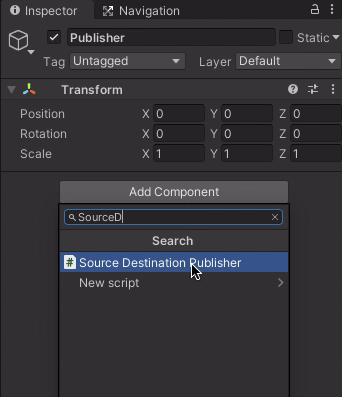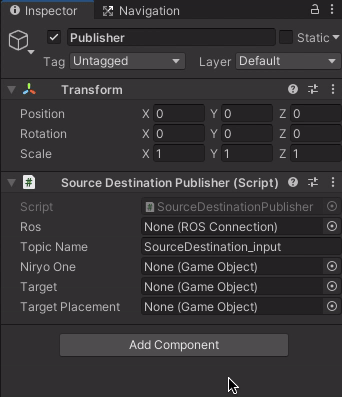
Publisher. Add the newly created SourceDestinationPublisher component to the Publisher GameObject by selecting the Publisher object. Click "Add Component" in the Inspector, and begin typing "SourceDestinationPublisher." Select the component when it appears.Note: Alternatively, you can drag the script from the Project window onto the Publisher object in the Hierarchy window.
-
Next, the object that will hold the TCP functionality needs to be added.
Create another GameObject, name it RosConnect, and add the script
Assets/Plugins/TCPConnector/ROSConnectionto it in the same way. -
Note that these components show empty member variables in the Inspector window, which need to be assigned.
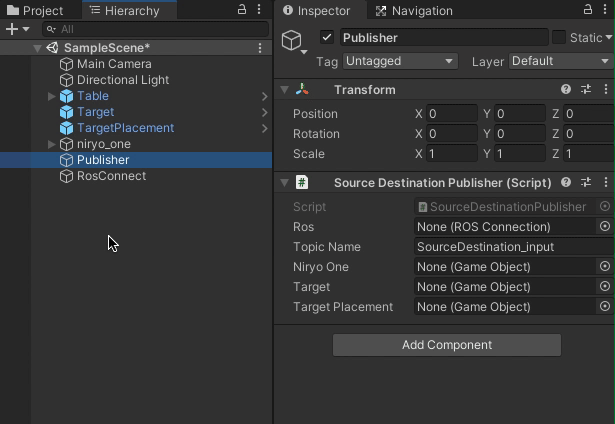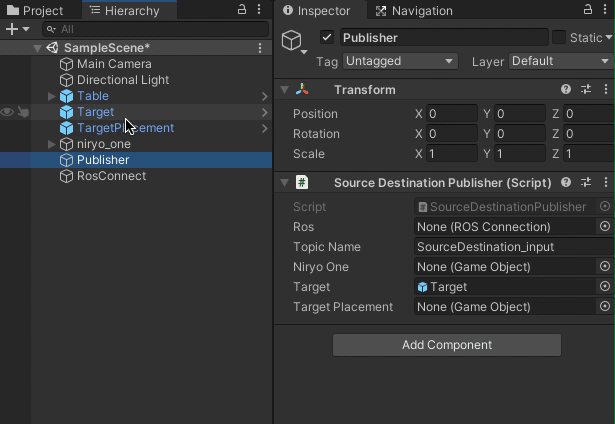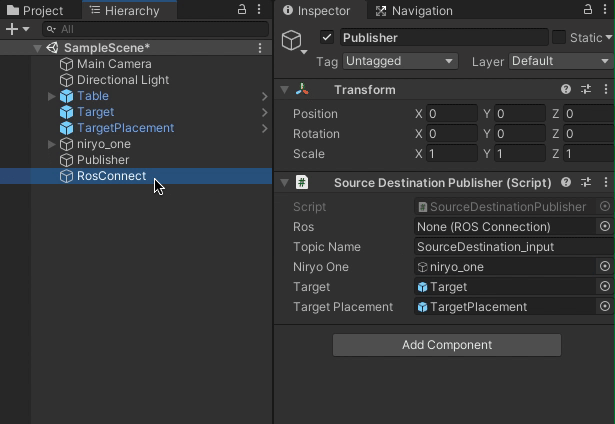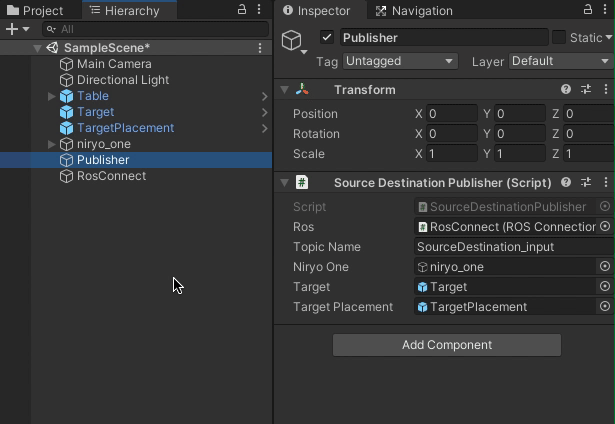
Select the Target object in the Hierarchy and assign it to the
Targetfield in the Publisher. Similarly, assign the TargetPlacement object to theTargetPlacementfield. Assign the niryo_one robot to theNiryo Onefield. Finally, assign the newly created RosConnect object to theRosfield. -
Once again, select the RosConnect object. The
Host Nameshould be the IP address of your ROS machine (not the one running Unity).-
Find the IP address of your ROS machine. In Ubuntu, open a terminal window, and enter
hostname -I. -
Replace the
Host Namevalue with the IP address of your ROS machine. Ensure that theHost Portis set to10000. -
If you are going to run ROS services with docker container introduced below, fill
Host NameandOverride Unity IPwith the loopback IP address127.0.0.1.
-
-
To call the
Publish()function, a UI element will be added for user input. In the Hierarchy window, right click to add a new UI > Button. Note that this will create a new Canvas parent as well.Note: In the
Gameview, you will see the button appear in the bottom left corner as an overlay. InSceneview the button will be rendered on a canvas object that may not be visible.Note: In case the Button does not start in the bottom left, it can be moved by setting the
Pos XandPos Yvalues in its Rect Transform component. For example, setting its Position to(-200, -200, 0)would set its position to the bottom right area of the screen. -
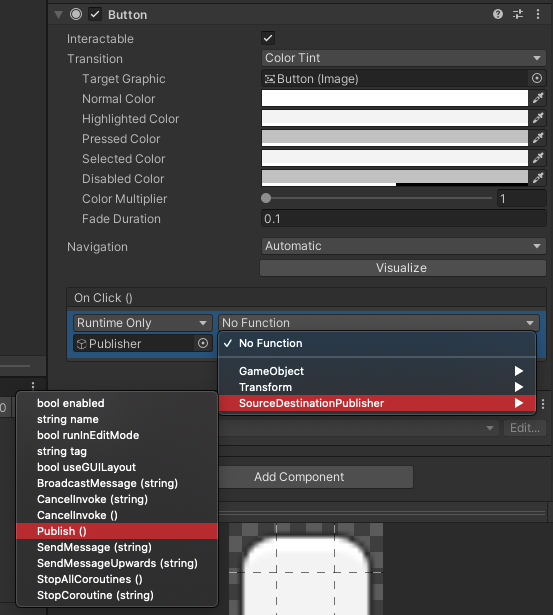
Select the newly made Button object, and scroll to see the Button component in the Inspector. Click the
+button under the emptyOnClick()header to add a new event. Select thePublisherobject in the Hierarchy window and drag it into the new OnClick() event, where it saysNone (Object). Click the dropdown where it saysNo Function. Select SourceDestinationPublisher >Publish(). -
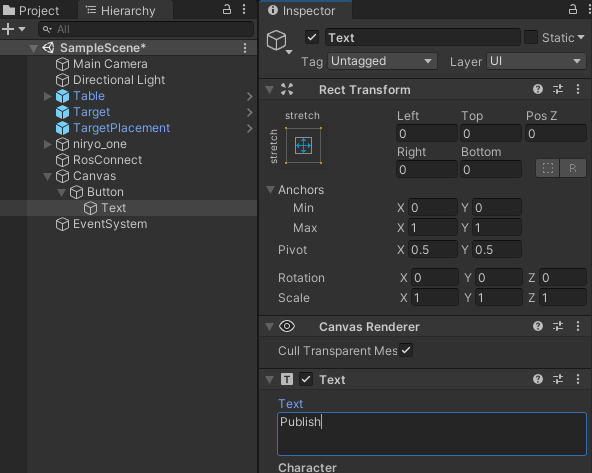
To change the text of the Button, expand the Button Hierarchy and select Text. Change the value in Text on the associated component.
The ROS side
Note: This project has been tested with Python 2 and ROS Melodic, as well as Python 3 and ROS Noetic.
Most of the ROS setup has been provided via the niryo_moveit package. This section will describe the .launch files and start the necessary ROS nodes for communication. Two methods are provideds to launch ROS nodes and services: either using a ROS docker container or doing it manually in your own ROS environment.
Use Docker Container
-
Build the ROS docker image
cd /YOUR/UNITY-ROBOTICS-HUB/REPOSITORY/tutorials/pick_and_place &&
git submodule update --init --recursive &&
docker build -t unity-robotics:pick-and-place -f docker/Dockerfile .
- Run ROS in a new docker container
docker run -it --rm -p 10000:10000 -p 5005:5005 unity-robotics:pick-and-place part_2 /bin/bash
- Terminate docker container
Press Ctrl + C or Cmd + C to terminate the docker container.
Manually Setup ROS
-
The provided files require the following packages to be installed. ROS Melodic users should run the following commands if the packages are not already present:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get install python-pip ros-melodic-robot-state-publisher ros-melodic-moveit ros-melodic-rosbridge-suite ros-melodic-joy ros-melodic-ros-control ros-melodic-ros-controllers ros-melodic-tf2-web-republisher sudo -H pip install rospkg jsonpickleROS Noetic users should run:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get install python3-pip ros-noetic-robot-state-publisher ros-noetic-moveit ros-noetic-rosbridge-suite ros-noetic-joy ros-noetic-ros-control ros-noetic-ros-controllers sudo -H pip3 install rospkg jsonpickleIn your ROS workspace, find the directory
src/niryo_moveit/scripts. Note the fileserver_endpoint.py. This script imports the necessary dependencies from tcp_endpoint and starts the server.rospy.spin()ensures the node does not exit until it is shut down.... tcp_server.start() rospy.spin() ...Additionally, note the file
src/niryo_moveit/scripts/trajectory_subscriber.py. This script subscribes to the SourceDestination topic. When something is published to this topic, this script will print out the information heard. -
If you have not already built and sourced the ROS workspace since importing the new ROS packages, navigate to your ROS workplace, and run
catkin_make && source devel/setup.bash. Ensure there are no errors. -
The ROS parameters will need to be set to your configuration in order to allow the server endpoint to fetch values for the TCP connection. Navigate to
src/niryo_moveit/config/params.yamland open the file for editing. You will need to know the IP address of your ROS machine as well as the IP address of the machine running Unity.-
The ROS machine IP, i.e.
ROS_IPshould be the same value as the one set asHost Nameon the RosConnect component in Unity. -
Update the
ROS_IPbelow with the appropriate addresses and copy the contents into theparams.yamlfile.ROS_IP: <your ROS IP>e.g.
ROS_IP: 192.168.50.149Note: Learn more about the server endpoint and ROS parameters here.
This YAML file is
rosparam setfrom the launch files provided for this tutorial, which has been copied below for reference. Additionally, the server_endpoint and trajectory_subscriber nodes are launched from this file.<launch> <rosparam file="$(find niryo_moveit)/config/params.yaml" command="load"/> <node name="server_endpoint" pkg="niryo_moveit" type="server_endpoint.py" args="--wait" output="screen" respawn="true" /> <node name="trajectory_subscriber" pkg="niryo_moveit" type="trajectory_subscriber.py" args="--wait" output="screen"/> </launch>Note: The launch files for this project are available in the package's
launchdirectory, i.e.src/niryo_moveit/launch/. -
-
Open a new terminal window in the ROS workspace. Once again, source the workspace. Then, run the following
roslaunchin order to set the ROS parameters, start the server endpoint, and start the trajectory subscriber.roslaunch niryo_moveit part_2.launchNote: Running
roslaunchautomatically starts ROS Core if it is not already running.This launch will print various messages to the console, including the set parameters and the nodes launched.
Ensure that the
process[server_endpoint]andprocess[trajectory_subscriber]were successfully started, and that a message similar to[INFO] [1603488341.950794]: Starting server on 192.168.50.149:10000is printed. -
Return to Unity, and press Play. Click the UI Button in the Game view to call SourceDestinationPublisher's
Publish()function, publishing the associated data to the ROS topic. View the terminal in which theroslaunchcommand is running. It should now printI heard:with the data.
ROS and Unity have now successfully connected!
Troubleshooting
-
If the error
[rosrun] Found the following, but they're either not files, or not executable: server_endpoint.pyappears, the Python script may need to be marked as executable viachmod +x Unity-Robotics-Hub/tutorials/pick_and_place/ROS/src/niryo_moveit/scripts/server_endpoint.py. -
...failed because unknown error handler name 'rosmsg'This is due to a bug in an outdated package version. Try runningsudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgradeto upgrade. -
If Unity fails to find a network connection, ensure that the ROS IP address is entered correctly as the Host Name in the RosConnect in Unity, and that the
src/niryo_moveit/config/params.yamlvalues are set correctly.
Resources
-
Setting up a ROS workspace:
Note: this tutorial was made using ROS Melodic.
-
More on ROS Topics
-
ROS TCP Connector package
-
TCP Endpoint package