6.1 KiB
Brains
The Brain encapsulates the decision making process. Brain objects must be children of the Academy in the Unity scene hierarchy. Every Agent must be assigned a Brain, but you can use the same Brain with more than one Agent.
Use the Brain class directly, rather than a subclass. Brain behavior is determined by the Brain Type. ML-Agents defines four Brain Types:
- External — The External and Internal types typically work together; set External when training your agents. You can also use the External brain to communicate with a Python script via the Python
UnityEnvironmentclass included in the Python portion of the ML-Agents SDK. - Internal – Set Internal to make use of a trained model.
- Heuristic – Set Heuristic to hand-code the agent's logic by extending the Decision class.
- Player – Set Player to map keyboard keys to agent actions, which can be useful to test your agent code.
Each of these types is an implementation of the CoreBrain interface. You can extend the CoreBrain class to create different brain types if the four built-in types don't do what you need.
During training, set your agent's brain type to External. To use the trained model, import the model file into the Unity project and change the brain type to Internal.
The Brain class has several important properties that you can set using the Inspector window. These properties must be appropriate for the agents using the brain. For example, the Vector Observation Space Size property must match the length of the feature vector created by an agent exactly. See Agents for information about creating agents and setting up a Brain instance correctly.
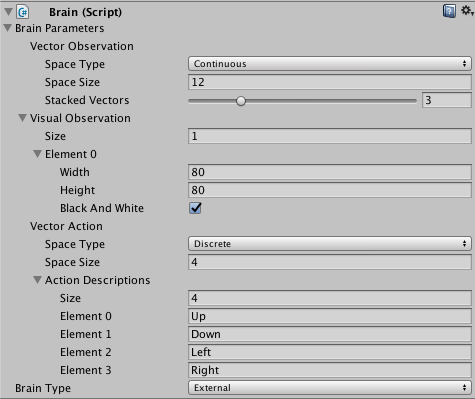
Brain Properties
The Brain Inspector window in the Unity Editor displays the properties assigned to a Brain component:
Brain Parameters- Define vector observations, visual observation, and vector actions for the Brain.Vector ObservationSpace Type- Corresponds to whether the observation vector contains a single integer (Discrete) or a series of real-valued floats (Continuous).Space Size- Length of vector observation for brain (In Continuous space type). Or number of possible values (in Discrete space type).Stacked Vectors- The number of previous vector observations that will be stacked before being sent to the brain.
Visual Observations- Describes height, width, and whether to greyscale visual observations for the Brain.Vector ActionSpace Type- Corresponds to whether action vector contains a single integer (Discrete) or a series of real-valued floats (Continuous).Space Size- Length of action vector for brain (In Continuous state space). Or number of possible values (in Discrete action space).Action Descriptions- A list of strings used to name the available actions for the Brain.
Type of Brain- Describes how the Brain will decide actions.External- Actions are decided by an external process, such as the PPO training process.Internal- Actions are decided using internal TensorFlowSharp model.Player- Actions are decided using Player input mappings.Heuristic- Actions are decided using customDecisionscript, which must be attached to the Brain game object.
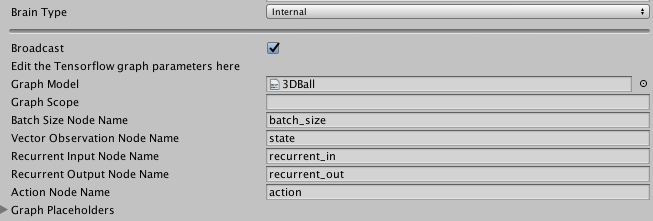
Internal Brain
Graph Model: This must be thebytesfile corresponding to the pretrained Tensorflow graph. (You must first drag this file into your Resources folder and then from the Resources folder into the inspector)Graph Scope: If you set a scope while training your TensorFlow model, all your placeholder name will have a prefix. You must specify that prefix here.Batch Size Node Name: If the batch size is one of the inputs of your graph, you must specify the name if the placeholder here. The brain will make the batch size equal to the number of agents connected to the brain automatically.Vector Observation Node Name: If your graph uses a vector observation as an input, you must specify the name if the placeholder here.Recurrent Input Node Name: If your graph uses a recurrent input / memory as input and outputs new recurrent input / memory, you must specify the name if the input placeholder here.Recurrent Output Node Name: If your graph uses a recurrent input / memory as input and outputs new recurrent input / memory, you must specify the name if the output placeholder here.Visual Observation Placeholder Name: If your graph uses observations as input, you must specify it here. Note that the number of observations is equal to the length ofCamera Resolutionsin the brain parameters.Action Node Name: Specify the name of the placeholder corresponding to the actions of the brain in your graph. If the action space type is continuous, the output must be a one dimensional tensor of float of lengthAction Space Size, if the action space type is discrete, the output must be a one dimensional tensor of int of length 1.Graph Placeholder: If your graph takes additional inputs that are fixed (example: noise level) you can specify them here. Note that in your graph, these must correspond to one dimensional tensors of int or float of size 1.Name: Corresponds to the name of the placeholdder.Value Type: Either Integer or Floating Point.Min ValueandMax Value: Specify the range of the value here. The value will be sampled from the uniform distribution ranging fromMin ValuetoMax Valueinclusive.
Player Brain
The Brain property settings must match the Agent implementation. For example, if you specify that the Brain use the Continuous State Space and a State Size of 23, then the Agent must provide a state vector with 23 elements. See Agents for more information about programming agents.