# Installing ML-Agents Toolkit for Windows (Deprecated)
:warning: **Note:** We no longer use this guide ourselves and so it may not work
correctly. We've decided to keep it up just in case it is helpful to you.
The ML-Agents Toolkit supports Windows 10. While it might be possible to run the
ML-Agents Toolkit using other versions of Windows, it has not been tested on
other versions. Furthermore, the ML-Agents Toolkit has not been tested on a
Windows VM such as Bootcamp or Parallels.
To use the ML-Agents Toolkit, you install Python and the required Python
packages as outlined below. This guide also covers how set up GPU-based training
(for advanced users). GPU-based training is not currently required for the
ML-Agents Toolkit. However, training on a GPU might be required by future
versions and features.
## Step 1: Install Python via Anaconda
[Download](https://www.anaconda.com/download/#windows) and install Anaconda for
Windows. By using Anaconda, you can manage separate environments for different
distributions of Python. Python 3.6.1 or higher is required as we no longer
support Python 2. In this guide, we are using Python version 3.6 and Anaconda
version 5.1
([64-bit](https://repo.continuum.io/archive/Anaconda3-5.1.0-Windows-x86_64.exe)
or [32-bit](https://repo.continuum.io/archive/Anaconda3-5.1.0-Windows-x86.exe)
direct links).
We recommend the default _advanced installation options_. However, select the
options appropriate for your specific situation.
After installation, you must open **Anaconda Navigator** to finish the setup.
From the Windows search bar, type _anaconda navigator_. You can close Anaconda
Navigator after it opens.
If environment variables were not created, you will see error "conda is not
recognized as internal or external command" when you type `conda` into the
command line. To solve this you will need to set the environment variable
correctly.
Type `environment variables` in the search bar (this can be reached by hitting
the Windows key or the bottom left Windows button). You should see an option
called **Edit the system environment variables**.
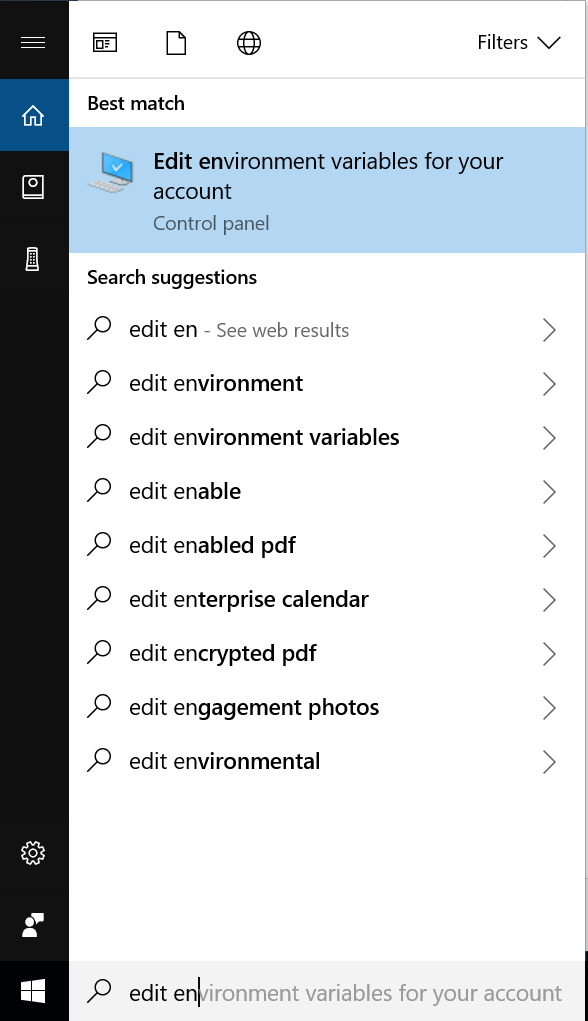
From here, click the **Environment Variables** button. Double click "Path" under
**System variable** to edit the "Path" variable, click **New** to add the
following new paths.
```console
%UserProfile%\Anaconda3\Scripts
%UserProfile%\Anaconda3\Scripts\conda.exe
%UserProfile%\Anaconda3
%UserProfile%\Anaconda3\python.exe
```
## Step 2: Setup and Activate a New Conda Environment
You will create a new [Conda environment](https://conda.io/docs/) to be used
with the ML-Agents Toolkit. This means that all the packages that you install
are localized to just this environment. It will not affect any other
installation of Python or other environments. Whenever you want to run
ML-Agents, you will need activate this Conda environment.
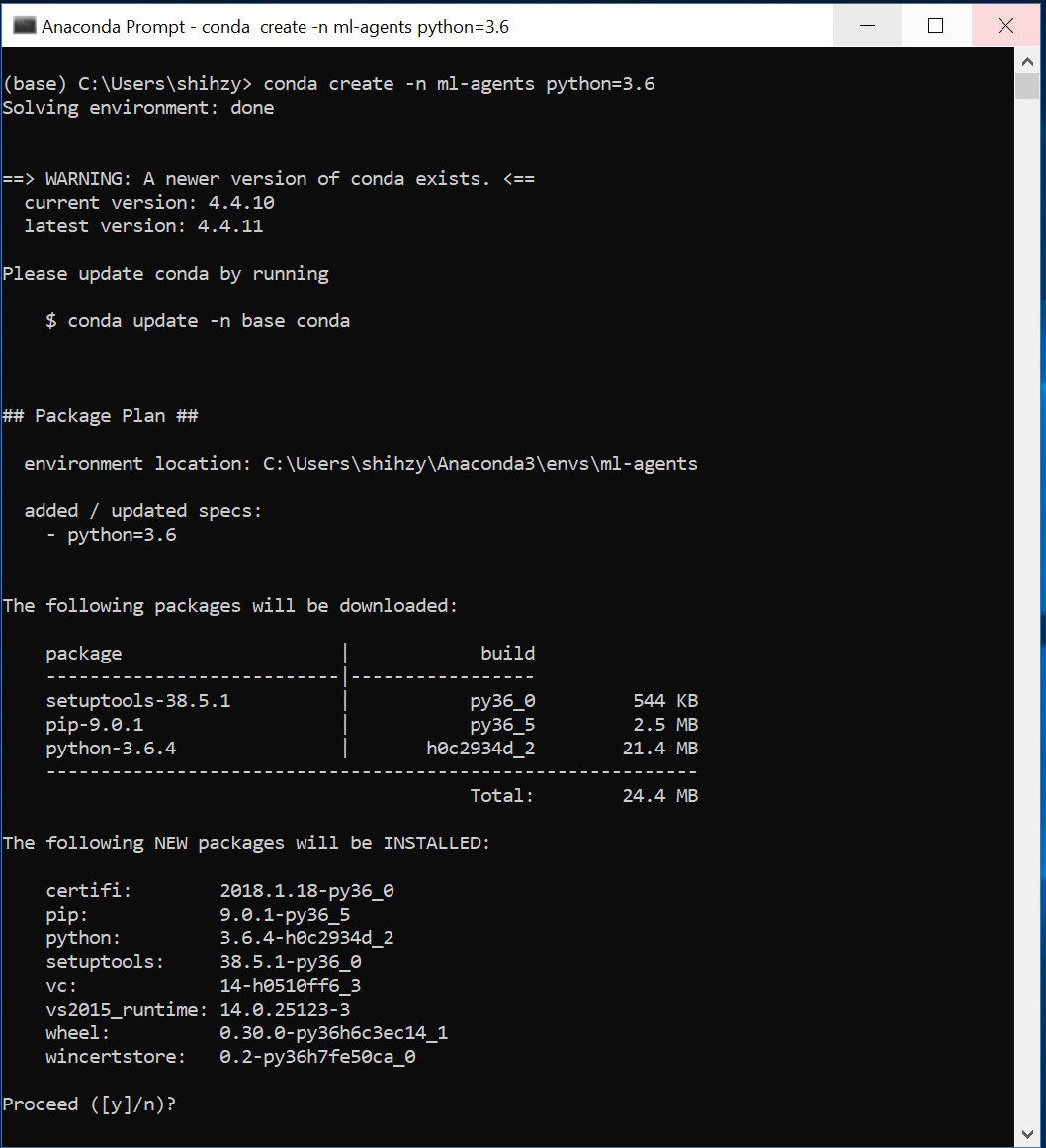
To create a new Conda environment, open a new Anaconda Prompt (_Anaconda Prompt_
in the search bar) and type in the following command:
```sh
conda create -n ml-agents python=3.6
```
You may be asked to install new packages. Type `y` and press enter _(make sure
you are connected to the Internet)_. You must install these required packages.
The new Conda environment is called ml-agents and uses Python version 3.6.
To use this environment, you must activate it. _(To use this environment In the
future, you can run the same command)_. In the same Anaconda Prompt, type in the
following command:
```sh
activate ml-agents
```
You should see `(ml-agents)` prepended on the last line.
Next, install `tensorflow`. Install this package using `pip` - which is a
package management system used to install Python packages. Latest versions of
TensorFlow won't work, so you will need to make sure that you install version
1.7.1. In the same Anaconda Prompt, type in the following command _(make sure
you are connected to the Internet)_:
```sh
pip install tensorflow==1.7.1
```
## Step 3: Install Required Python Packages
The ML-Agents Toolkit depends on a number of Python packages. Use `pip` to
install these Python dependencies.
If you haven't already, clone the ML-Agents Toolkit Github repository to your
local computer. You can do this using Git
([download here](https://git-scm.com/download/win)) and running the following
commands in an Anaconda Prompt _(if you open a new prompt, be sure to activate
the ml-agents Conda environment by typing `activate ml-agents`)_:
```sh
git clone --branch release_12 https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/ml-agents.git
```
The `--branch release_12` option will switch to the tag of the latest stable
release. Omitting that will get the `master` branch which is potentially
unstable.
If you don't want to use Git, you can find download links on the
[releases page](https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/ml-agents/releases).
The `com.unity.ml-agents` subdirectory contains the core code to add to your
projects. The `Project` subdirectory contains many
[example environments](Learning-Environment-Examples.md) to help you get
started.
The `ml-agents` subdirectory contains a Python package which provides deep
reinforcement learning trainers to use with Unity environments.
The `ml-agents-envs` subdirectory contains a Python API to interface with Unity,
which the `ml-agents` package depends on.
The `gym-unity` subdirectory contains a package to interface with OpenAI Gym.
Keep in mind where the files were downloaded, as you will need the trainer
config files in this directory when running `mlagents-learn`. Make sure you are
connected to the Internet and then type in the Anaconda Prompt:
```console
pip install mlagents
```
This will complete the installation of all the required Python packages to run
the ML-Agents Toolkit.
Sometimes on Windows, when you use pip to install certain Python packages, the
pip will get stuck when trying to read the cache of the package. If you see
this, you can try:
```console
pip install mlagents --no-cache-dir
```
This `--no-cache-dir` tells the pip to disable the cache.
### Installing for Development
If you intend to make modifications to `ml-agents` or `ml-agents-envs`, you
should install the packages from the cloned repo rather than from PyPi. To do
this, you will need to install `ml-agents` and `ml-agents-envs` separately.
In our example, the files are located in `C:\Downloads`. After you have either
cloned or downloaded the files, from the Anaconda Prompt, change to the
ml-agents subdirectory inside the ml-agents directory:
```console
cd C:\Downloads\ml-agents
```
From the repo's main directory, now run:
```console
cd ml-agents-envs
pip install -e .
cd ..
cd ml-agents
pip install -e .
```
Running pip with the `-e` flag will let you make changes to the Python files
directly and have those reflected when you run `mlagents-learn`. It is important
to install these packages in this order as the `mlagents` package depends on
`mlagents_envs`, and installing it in the other order will download
`mlagents_envs` from PyPi.
## (Optional) Step 4: GPU Training using The ML-Agents Toolkit
GPU is not required for the ML-Agents Toolkit and won't speed up the PPO
algorithm a lot during training(but something in the future will benefit from
GPU). This is a guide for advanced users who want to train using GPUs.
Additionally, you will need to check if your GPU is CUDA compatible. Please
check Nvidia's page [here](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus).
Currently for the ML-Agents Toolkit, only CUDA v9.0 and cuDNN v7.0.5 is
supported.
### Install Nvidia CUDA toolkit
[Download](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive) and install the
CUDA toolkit 9.0 from Nvidia's archive. The toolkit includes GPU-accelerated
libraries, debugging and optimization tools, a C/C++ (Step Visual Studio 2017)
compiler and a runtime library and is needed to run the ML-Agents Toolkit. In
this guide, we are using version
[9.0.176](https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/9.0/Prod/network_installers/cuda_9.0.176_win10_network-exe)).
Before installing, please make sure you **close any running instances of Unity
or Visual Studio**.
Run the installer and select the Express option. Note the directory where you
installed the CUDA toolkit. In this guide, we installed in the directory
`C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.0`
### Install Nvidia cuDNN library
[Download](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) and install the cuDNN library
from Nvidia. cuDNN is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural
networks. Before you can download, you will need to sign up for free to the
Nvidia Developer Program.
Once you've signed up, go back to the cuDNN
[downloads page](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn). You may or may not be
asked to fill out a short survey. When you get to the list cuDNN releases,
**make sure you are downloading the right version for the CUDA toolkit you
installed in Step 1.** In this guide, we are using version 7.0.5 for CUDA
toolkit version 9.0
([direct link](https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/cudnn/secure/v7.0.5/prod/9.0_20171129/cudnn-9.0-windows10-x64-v7)).
After you have downloaded the cuDNN files, you will need to extract the files
into the CUDA toolkit directory. In the cuDNN zip file, there are three folders
called `bin`, `include`, and `lib`.
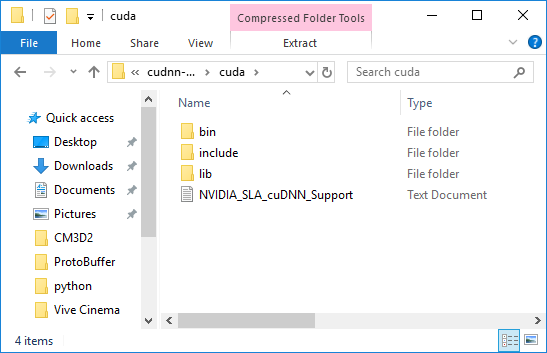
Copy these three folders into the CUDA toolkit directory. The CUDA toolkit
directory is located at
`C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.0`
### Set Environment Variables
You will need to add one environment variable and two path variables.
To set the environment variable, type `environment variables` in the search bar
(this can be reached by hitting the Windows key or the bottom left Windows
button). You should see an option called **Edit the system environment
variables**.

From here, click the **Environment Variables** button. Click **New** to add a
new system variable _(make sure you do this under **System variables** and not
User variables_.
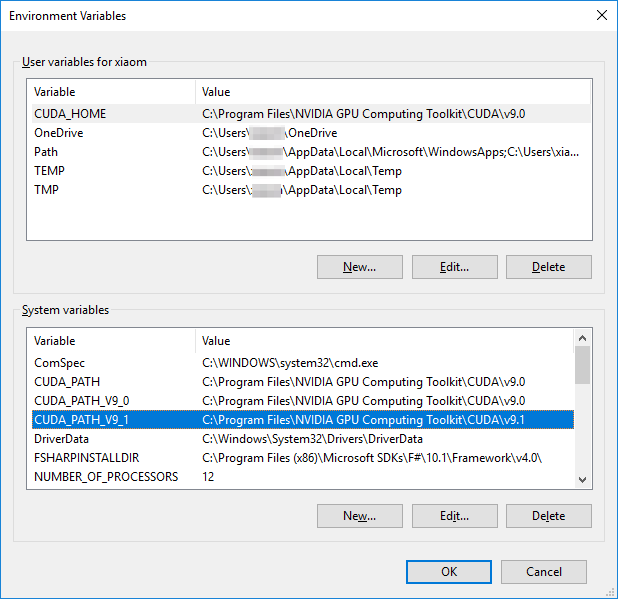
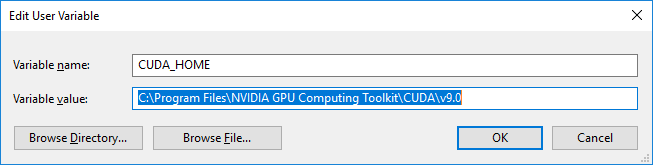
For **Variable Name**, enter `CUDA_HOME`. For the variable value, put the
directory location for the CUDA toolkit. In this guide, the directory location
is `C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.0`. Press **OK** once.
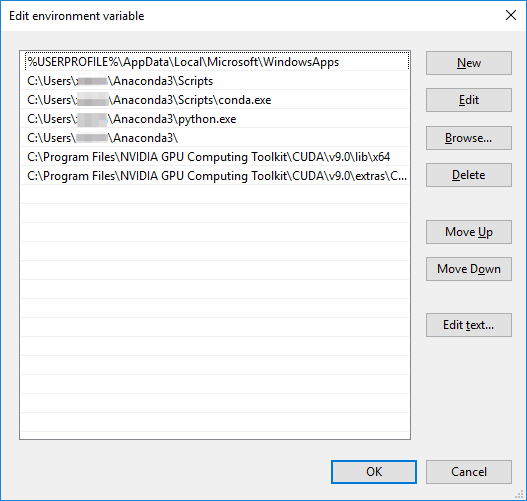
To set the two path variables, inside the same **Environment Variables** window
and under the second box called **System Variables**, find a variable called
`Path` and click **Edit**. You will add two directories to the list. For this
guide, the two entries would look like:
```console
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.0\lib\x64
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.0\extras\CUPTI\libx64
```
Make sure to replace the relevant directory location with the one you have
installed. _Please note that case sensitivity matters_.
### Install TensorFlow GPU
Next, install `tensorflow-gpu` using `pip`. You'll need version 1.7.1. In an
Anaconda Prompt with the Conda environment ml-agents activated, type in the
following command to uninstall TensorFlow for cpu and install TensorFlow for gpu
_(make sure you are connected to the Internet)_:
```sh
pip uninstall tensorflow
pip install tensorflow-gpu==1.7.1
```
Lastly, you should test to see if everything installed properly and that
TensorFlow can identify your GPU. In the same Anaconda Prompt, open Python in
the Prompt by calling:
```sh
python
```
And then type the following commands:
```python
import tensorflow as tf
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True))
```
You should see something similar to:
```console
Found device 0 with properties ...
```
## Acknowledgments
We would like to thank
[Jason Weimann](https://unity3d.college/2017/10/25/machine-learning-in-unity3d-setting-up-the-environment-tensorflow-for-agentml-on-windows-10/)
and
[Nitish S. Mutha](http://blog.nitishmutha.com/tensorflow/2017/01/22/TensorFlow-with-gpu-for-windows.html)
for writing the original articles which were used to create this guide.


